5 Research-Backed Strategies to Build Reading Fluency That Actually Work
If your students are stuck reading word by word—or guessing instead of decoding—you’re not alone. Building reading fluency is one of the most common challenges teachers face. But here’s the good news: fluency isn’t about speed. It’s about accuracy, expression, and comprehension. In this post, you’ll learn five simple, research-backed strategies to help your students move from slow, choppy reading to confident, expressive fluency. Whether you're teaching early readers or supporting students who need extra practice, these fluency tools will make a difference—without adding stress to your day.
What Is Reading Fluency—and Why It Matters
Fluency is more than just fast reading—it’s the ability to read with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression, all while understanding what’s being read. According to the National Reading Panel, fluency acts as a bridge between decoding and comprehension. When students struggle with fluency, it can be a sign that they need additional support in phonics, decoding, or practice with connected text.
5 Strategies to Build Reading Fluency That Work in Real Classrooms
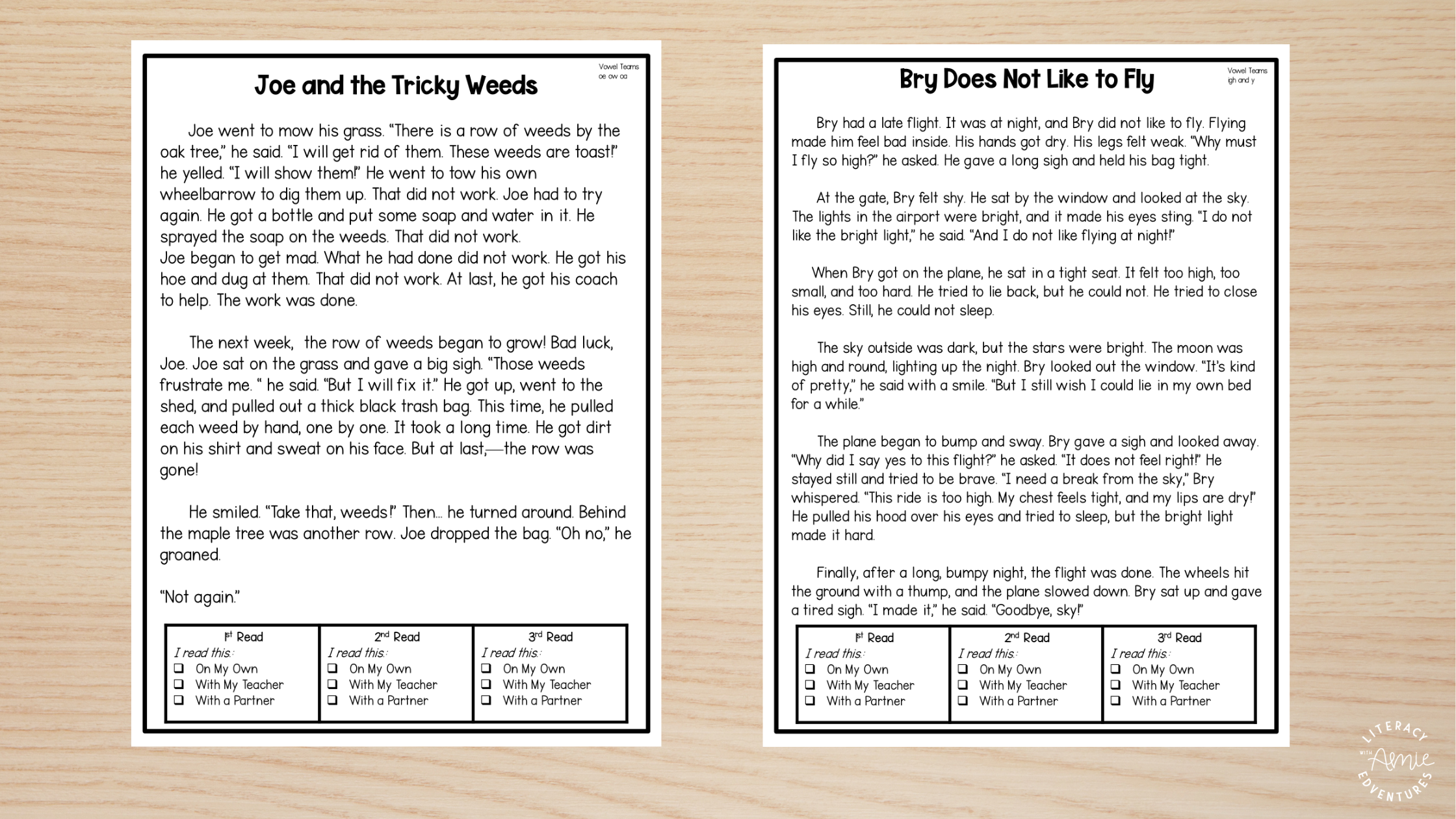
1. Repeated Reading of Decodable Texts
Why it works: There’s a common misconception that students should read a book or passage once and move on. But fluency is built through repetition. Each time a student revisits a text, they strengthen word recognition, reinforce phonics patterns, and improve rate and prosody.
Reading a text once builds familiarity. Reading it again builds fluency.
How to use it:
Choose a short, decodable passage aligned with your phonics instruction.
Model fluent reading first, emphasizing phrasing and expression.
Invite students to read it multiple times over the week—independently, chorally, or with a partner.
Track progress with timers, highlight target words, or set fluency goals.
🌟 Fluency Tip: Repetition increases exposure—and the more times a student sees a word, the more likely they are to read it automatically. That’s how we build fluency.
2. Echo Reading
Why it works: Echo reading is one of the most effective assisted reading strategies, especially for early or hesitant readers. In echo reading, the teacher reads a line aloud with expression, and the student repeats it—just like an echo. This allows students to hear what fluent reading sounds like and practice it right away.
It’s not just effective—it’s research-backed. The National Reading Panel (2000) highlighted assisted reading (which includes echo reading) as a proven method to boost fluency. Later research by Rasinski & Samuels (2011) and Kuhn & Stahl (2003) confirmed that echo reading improves accuracy, rate, and prosody, especially when paired with phonics instruction.
How to use it:
Choose short, decodable texts or fluency sentences.
Read a line aloud using proper phrasing and tone.
Students repeat the line, mimicking your expression.
Repeat this across the passage or poem.
🌟 Fluency Tip: Echo reading is a confidence-booster. It gives students a safety net while helping them internalize patterns of fluent reading.
3. Fluency Pyramids
Why it works: Fluency pyramids are a low-prep, high-impact way to help students build automaticity and confidence at the sentence level. They reduce overwhelm by introducing one word at a time while providing multiple exposures to each.
Example:
we
we can
we can jump
we can jump high
Each layer adds one more word, allowing for smooth repetition and building toward complete sentence reading.
How to use it:
Use pyramids as a warm-up during small groups or literacy stations.
Align the words with your phonics skill of the week.
Have students read top to bottom multiple times, each time building fluency and expression.
🌟 Fluency Tip: This strategy is especially helpful for early readers who benefit from structure and repetition.
4. Phrase-Cued Reading
Why it works: Fluent readers don’t read word by word—they read in phrases, grouping words naturally to reflect meaning. This skill, known as prosody, supports both reading fluency and comprehension.
Phrase-cued reading helps students recognize those meaningful chunks, often called "thought units." It teaches them where to pause, how to group words, and how to attend to punctuation cues.
How to use it:
Start with a short sentence or passage.
Add slashes or scooping lines to mark phrases.
Read it aloud first with phrasing.
Have students practice on their own, then with a partner.
Example: Instead of: the / dog / ran / down / the / hill
Try: the dog / ran down the hill
🌟 Fluency Tip: Use color-coded phrases or allow students to “scoop” phrases with markers to reinforce the concept.
5. Performance Reading
Why it works: When students know they’ll be reading aloud for an audience—whether it's a partner, small group, or the whole class—they automatically pay more attention to expression and pacing. Performance reading gives a purpose to fluency practice.
It also taps into motivation and engagement, helping students read with confidence and joy.
How to use it:
Use reader’s theater, short poems, or decodable sentences.
Let students choose a “performance piece” to practice all week.
Rehearse it through repeated reading, echo reading, or partner reading.
Celebrate with a performance on Friday!
🌟 Fluency Tip: Record students reading and let them watch their progress. It’s a powerful tool for reflection and growth.
Final Thoughts
Reading fluency is not optional—it’s essential. When students read fluently, they can focus on understanding, thinking critically, and enjoying what they read.
But fluency doesn’t magically appear. It’s built intentionally through modeling, practice, and meaningful instruction. With just a few consistent routines—like repeated reading, echo reading, fluency pyramids, phrased reading, and performance—you can transform your students into expressive, confident readers.
👉 Want a step-by-step system that makes fluency instruction easy, engaging, and effective?
Join the Route2Reading Membership—you’ll get access to done-for-you phonics lessons, fluency resources, decodable texts, and so much more. It’s everything you need to support your readers from sounds to sentences—and beyond.